 |
| Outline
of the long-term care insurance system |
 |
 |
 |
| |
 |
|
Long-term care insurance is a social insurance system to provide long-term care services to persons experiencing difficulties in their daily lives due to physical impairments resulting from advanced age. |
 |
|
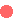 How the long-term
care insurance system is structured How the long-term
care insurance system is structured
|
 |
|
 Administration of
the long-term care insurance system Administration of
the long-term care insurance system
|
 |
|
Municipal authorities act as administrators of the long-term
care insurance system. Municipalities covered include cities,
towns and villages plus the 23 special metropolitan wards of
Tokyo. These authorities administer the insurance system according
to the circumstances in their respective areas. Medical care
insurance and pension providers such as the state, prefectures,
and Health Insurance Societies support the long-term care insurance
system in a variety of ways.
|
|
 Insured persons Insured persons
|
 |
|
The long-term care insurance system covers everyone aged 40
or over. Age-related ailments begin to occur at this age, a problem
that coincides with the increasing need to look after parents.
As long-term care begins to be a fact of life after the age of
40, this age is set as the starting age for beneficiaries under
the system.
The long-term care insurance system divides insured persons into two
groups: (1) persons aged 65 years or over and (2) persons aged between
40 and 64 who are covered by medical care insurance. The former group
is referred to as "category 1 insured persons." The latter
group is known as "category 2 insured persons." The system
also covers people classified under the health insurance system as dependents.
There are persons outside of the long-term care insurance system. Check
here for details >> "When
you no longer qualify for long-term care insurance"
|
|
 |
|
 |
