 |
| When you
use the long-term care insurance services |
 |
 |
 |
| |
 |
|
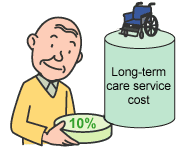 Copayments for long-term care services will be 10% - 30% of the cost of the services. Copayments for long-term care services will be 10% - 30% of the cost of the services.
|
|
 Individuals pay 10% - 30% of service costs Individuals pay 10% - 30% of service costs
|
 |
Copayments for long-term care services will be 10% (20% or 30% for high-income earners) of the cost of the services, depending on the user's ability to pay. For in-home care services, you will also be required to pay meal expenses and living expenses. Those receiving inpatient services in long-term care facilities will also be required to pay meal expenses and accommodation expenses. Measures are available to reduce such costs for low-income earners.
You can check your copayment on the Long-term Care Insurance Copayment Certificate issued to persons needing support or long-term care.
[Category 1 insured persons with copayments of 20% or 30%]
Copayment |
Income standard |
20% |
- Total income of the person: 1.6 million yen or more,
- Pension income + other total income of Category 1 insured persons in the same household: 2.8 million yen or more for a single-person household, 3.46 million yen or more for a household of two or more persons
|
30% |
- Total income of the person: 2.2 million yen or more,
- Pension income + other total income of Category 1 insured persons in the same household: 3.4 million yen or more for a single-person household, 4.63 million yen or more for a household of two or more persons
|
|
* Notwithstanding the above, copayments are 10% for Category 2 insured persons, those exempt from paying municipal tax, and those receiving public assistance. |
|
 Cases in which individual
cost-sharing grow large Cases in which individual
cost-sharing grow large
|
 |
A monthly maximum applies to cost-sharing for long-term care per household, based on income. The maximum copayment for ordinary households subject to resident tax(*) and households including persons earning income at levels comparable to active workers is 44,400 yen (lower for low-income earners). You are eligible to be reimbursed for any amount beyond this maximum as high long-term care service costs. Note that the accommodation expenses and meal expenses
associated with services at care
facilities are not eligible for reimbursement as part of high-cost
long-term care expenses.
In addition, when total co-payments for health insurance and long-term care insurance paid over the course of a single year are remarkably high, you can receive benefits to defray the high aggregate cost for long-term care services.
See here for more information: In cases in which the total co-payments for medical care and long-term care are remarkably high.
* Until the end of July 2020, the annual maximum amount is 446,400 yen for households in which all individuals make copayments of 10%. |
|
 Category 2 insured
persons may receive these benefits subject to certain conditions Category 2 insured
persons may receive these benefits subject to certain conditions
|
 |
|
Category 2 insured persons (persons aged between 40 and 64)
may receive services under long-term care insurance only if they
require long-term care for age-related conditions (specified
diseases and disorders). Such persons cannot receive benefits
under long-term care insurance in cases where he or she requires
long-term care for a condition resulting from a traffic accident.
|
|
 Specified diseases
and disorders for which Category 2 insured persons may receive
such services Specified diseases
and disorders for which Category 2 insured persons may receive
such services
|
 |
|
(1)
|
Pre-acknowledge syndrome (senile dementia)
|
 |
 |
|
(2)
|
Cerebrovascular disease
|
 |
 |
|
(3)
|
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, or Lou Gehrig's Disease)
|
 |
 |
|
(4)
|
Parkinson's disease-related conditions
|
 |
 |
|
(5)
|
Spinocerebellar degeneration
|
 |
 |
|
(6)
|
Multiple system atrophy
|
 |
 |
|
(7)
|
Diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy
|
 |
 |
|
(8)
|
Arteriosclerosis obliterans
|
 |
 |
|
(9)
|
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
|
 |
 |
|
(10)
|
Degenerative joint disease with pronounced deformation of both
knee or hip joints
|
 |
 |
|
(11)
|
Rheumatoid arthritis
|
 |
 |
|
(12)
|
Ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament
|
 |
 |
|
(13)
|
Stenochoria of the spinal canal
|
 |
 |
|
(14)
|
Fractures due to osteoporosis
|
 |
 |
|
(15)
|
Progeria (Werner syndrome)
|
 |
 |
|
(16)
|
Terminal cancer
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
